From Grok:
General Motors (GM) explored the Wankel rotary engine in the early 1970s, aiming to bring a two-rotor version, known as the General Motors Rotary Combustion Engine (GMRCE) or RC2-206, into production. Here’s a concise history of its development and intended use:
Background and Motivation
- Origins: The Wankel engine, invented by Felix Wankel, promised compact size, fewer moving parts (about 40% fewer than a comparable six-cylinder engine), smooth operation, and high power-to-weight ratio. Its potential led many automakers, including GM, to pursue it as a future powerplant.karlludvigsen.substack.com
- Licensing: In November 1970, GM paid $50 million (equivalent to ~$405 million in 2024) to Curtiss-Wright for licenses to develop and produce their version of the Wankel engine. GM President Ed Cole, a key advocate, saw it as a revolutionary alternative to traditional piston engines.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Leadership: The project was driven by Ed Cole, with support from Chevrolet executives Pete Estes and John DeLorean. Bob Templin led rotary-engine research at GM’s Tech Center in Warren, Michigan, with Cole personally overseeing progress.en.wikipedia.org
Development of the RC2-206
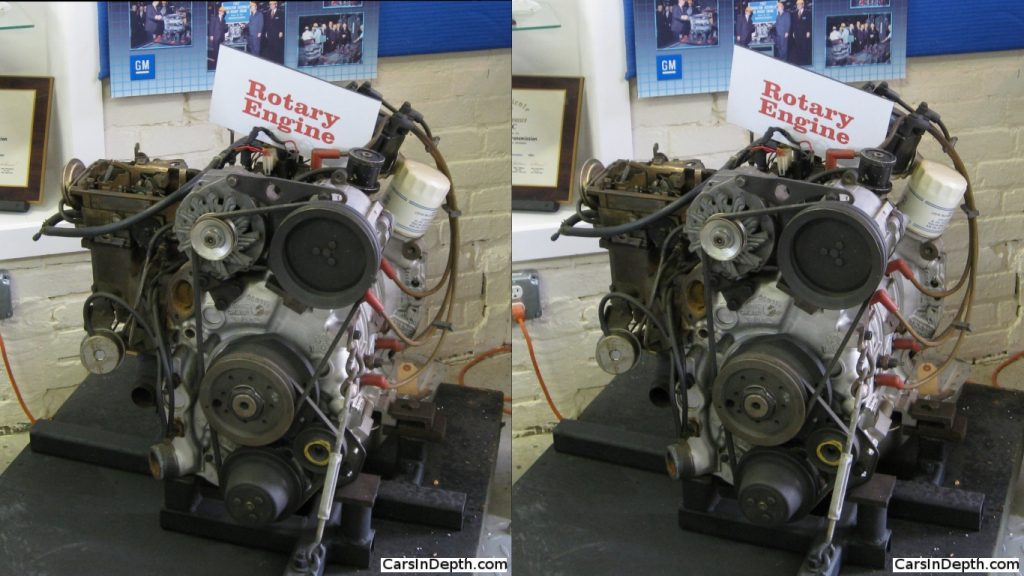
- Specifications: The RC2-206 was a two-rotor engine with a displacement of 206 cubic inches (3.38 liters), featuring twin distributors and coils. Initially, GM used cast-iron housings, but by August 1972, the design shifted to aluminum to improve heat dissipation and address rotor tip-seal wear, which became problematic after 15,000 miles in cast-iron configurations.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Reliability: GM’s testing showed the engine was durable, with prototypes running up to 500,000 miles with minimal wear, thanks to fewer moving parts compared to four-, six-, or eight-cylinder engines.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Target Vehicle: The engine was initially slated for the 1974 Chevrolet Vega, with an introduction planned for October 1973. Later, GM planned to showcase it in the 1975 Vega-based Monza 2+2. The engine produced around 180 horsepower, competitive for its size.en.wikipedia.orgmotortrend.comcapitalone.com
Testing and Prototypes
- Cold-Weather Testing: In 1973, RC2-206 engines were installed in Chevrolet Vegas for cold-weather testing in Canada, indicating progress toward production readiness.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Concept Vehicles: GM showcased the engine in prototypes like the XP-987 GT (Two-Rotor Corvette), a mid-engine concept debuted at the 1973 Frankfurt Auto Show. This concept, initially called the Chevrolet GT, used a shortened Porsche 914/6 chassis and produced 180 horsepower with a three-speed automatic transmission.motortrend.comgoodwood.com
Challenges and Cancellation
- Fuel Economy and Emissions: The Wankel’s poor thermal efficiency led to substandard fuel economy, a critical issue during the 1973-1974 Arab oil embargo, which spiked fuel prices. By November 1973, GM struggled to meet 1975 U.S. emissions standards, and no immediate solutions emerged despite intense efforts by Cole and engineer Frank Winchell.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Production Delays: On December 21, 1973, GM announced a postponement after paying an additional $10 million in license fees. Motor Trend predicted in April 1974 that if the engine wasn’t integrated into the 1975 lineup, it might never reach production.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Cancellation: In 1974, after Ed Cole’s retirement, his successor Pete Estes showed little interest in the Wankel. GM canceled the program, citing fuel economy and emissions issues, despite claims from the R&D team that they had solved the fuel economy problem and achieved engine lifespans exceeding 530,000 miles. These findings were not considered in the cancellation decision.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
- Impact on Partners: American Motors (AMC), which had designed the 1975 Pacer around GM’s rotary engine, was forced to reconfigure it with an inline-six engine after GM’s withdrawal.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.orgtractors.fandom.com
Legacy
- Near-Production Status: The RC2-206 was close to production, with finished castings and production-ready tooling at GM’s HydraMatic Division in Ypsilanti, Michigan. Photos from the Ypsilanti Automotive Heritage Museum show a polished, production-ready engine, not a rough prototype.rokemneedlearts.com
- Missed Opportunity: GM’s Wankel program was one of the most advanced among U.S. automakers, but the oil crisis, emissions challenges, and leadership changes halted it. Unlike Mazda, which persevered with rotary engines, GM abandoned the technology, leaving prototypes like the Two-Rotor Corvette and Vega as footnotes in automotive history.carbuzz.commotortrend.com
- Subsequent Concepts: GM also experimented with a four-rotor Wankel in the 1973 Aerovette concept, producing 355-420 horsepower, but it never progressed beyond the prototype stage due to the same issues.carbuzz.comgoodwood.com
Why It Failed
- Economic Context: The 1973 oil crisis made fuel efficiency critical, and the Wankel’s thirstiness was a liability.carbuzz.com
- Emissions Standards: Stricter U.S. regulations exposed the Wankel’s high exhaust emissions, which GM couldn’t resolve in time.en.wikipedia.orgcarbuzz.com
- Apex Seal Issues: Though GM addressed some reliability concerns, apex seal wear remained a challenge, as seen in other Wankel applications like NSU’s Ro 80.rotaryrevs.commotortrend.com
- Leadership Shift: The departure of Ed Cole, the project’s champion, and lack of enthusiasm from Pete Estes sealed its fate.en.wikipedia.orgen.m.wikipedia.org
